Authors
Peter Turcsanyi, R. Urbanová, A. Petráčková, Z. Kubová, Tomas Papajik, Eva Kriegová
Background
The therapeutic landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has significantly evolved with the development of targeted therapies. However, treatment options for patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL after BTK and BCL2 inhibitor failure remain limited. Idelalisib, a PI3Kδ inhibitor, represents a potential option in this setting, though its use is often limited by toxicity. We present a real-world retrospective analysis of idelalisib in R/R CLL patients.
Methods and characteristics
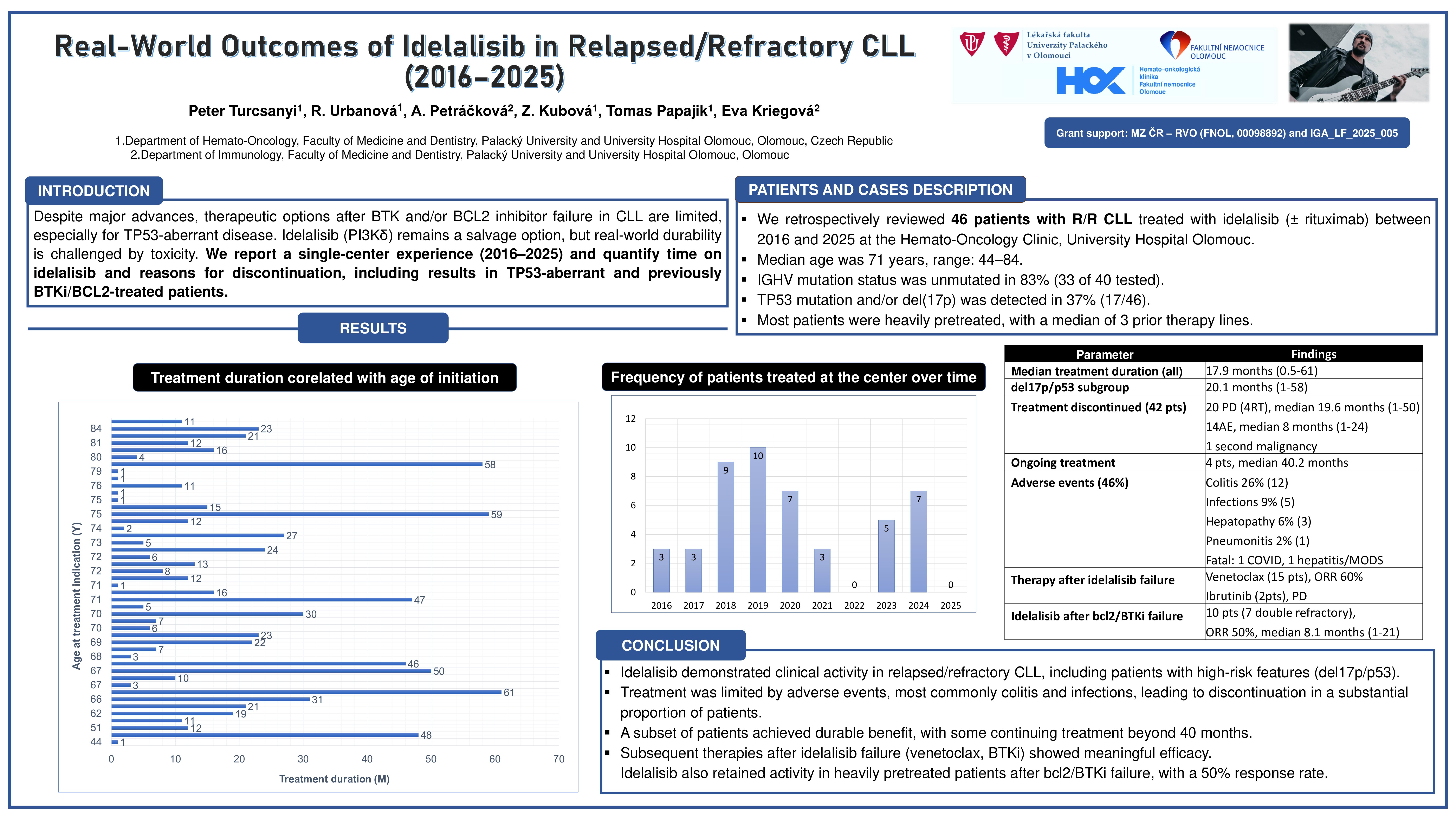
We retrospectively reviewed 46 patients with R/R CLL treated with idelalisib (± rituximab) between 2016 and early 2025 at the Hemato-Oncology Clinic, University Hospital Olomouc. Median age was 71 years, range: 44–84. IGHV mutation status was unmutated in 83% (33 of 40 tested). TP53 mutation and/or del(17p) was detected in 37% (17/46). Most patients were heavily pretreated, with a median of 3 prior therapy lines.
Results
The median duration of treatment with idelalisib among all treated patients was 17.6 months (range: 0.5–60 months) with ORR 77%. . In patients with del(17p)/TP53 mutation, the median treatment duration was 16.3 months (range: 1–55 months). Treatment was discontinued in 33 patients: 18 due to progressive disease (PD), including 4 cases of Richter’s transformation; median duration of treatment in this group was 16.7 months (range: 1–48 months). 13 due to adverse events (AEs), with a treatment duration of 15.3 months (range: 1–24 months). 1 patient discontinued due to cancer duplicity, and 1 due to complete remission (CR) and pneumonia.
In a subgroup of 10 patients who had previously received BTKi or BCL2i therapy (7 of whom were double-refractory), the overall response rate (ORR) was 50%, and the median treatment duration was 15 months (range: 1–16).
Among 15 patients treated with venetoclax following idelalisib failure, the ORR was 60%.
Adverse events (AEs) occurred in 46% of patients (21 out of 46). Colitis was observed in 26% (12 patients), infections in 9% (5 patients), hepatopathy in 6% (3 patients) and pneumonitis in 2% (1 patient). Fatal adverse events was observed in 2 pts: 1 patient died from COVID-19 and 1 patient died from hepatitis with subsequent multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS).
Conclusions
In this single-center real-world cohort, idelalisib demonstrated clinical activity in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, including those with high-risk genetic features and prior exposure to targeted therapies. While efficacy was modest in heavily pretreated patients, selected individuals derived clear benefit. Toxicity remains a significant limitation and underscores the need for careful monitoring. These results support a role for idelalisib in selected high-risk patients and highlight the unmet need for better-tolerated salvage options in R/R CLL.
Keywords : R/R CLL, BTKi/BCL2i refractory, idelalisib
Please indicate how this research was funded. : supported by grants: MZ ČR – RVO (FNOL, 00098892) and IGA_LF_2025_005
Please indicate the name of the funding organization.: supported by grants: MZ ČR – RVO (FNOL, 00098892) and IGA_LF_2025_005